Blog
We regularly update articles related to the prototyping and manufacturing industry. You’re welcome to check our previous blogs and subscribe to our newsletter.
CNC Machined Prototypes: From Digital Design to Tangible Reality
Prototyping, a critical phase in manufacturing, transforms ideas into tangible models for testing and refinement. CNC Machined Prototypes, a computer-driven technique, have revolutionized this stage by offering precise, rapid, and repeatable prototypes directly from digital designs, efficiently bridging the gap between concept and physical reality.
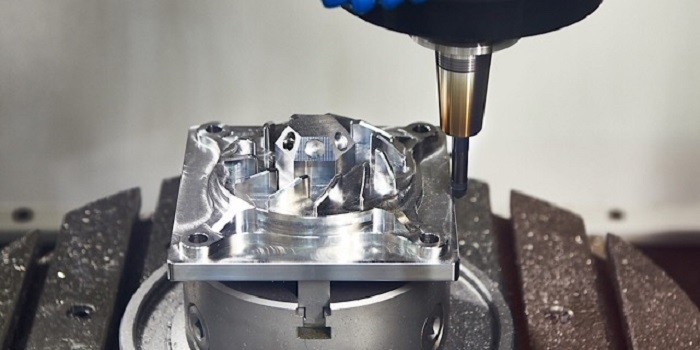
The CNC Machining Process
CNC machining, a subset of Computer Numerical Control processes, leverages computer-guided machinery to craft detailed components with remarkable accuracy. It stands out for its systematic transformation of digital blueprints into physical prototypes. The journey is as follows:
Digital Blueprint Formation
The birth of a CNC prototype is in the digital world. Through Computer-Aided Design (CAD) tools, designers draft intricate 3D visualizations of the prospective item. These digital drafts anchor the subsequent machining phases.
Transition to Machine Syntax (G-code)
Following the design stage, the digital model undergoes translation into a machine-readable format known as G-code. This conversion ensures the CNC equipment receives explicit commands, guaranteeing each action — be it a cut, drill, or etch — aligns seamlessly with the initial design.
Material Determination
CNC apparatuses boast adaptability and are compatible with various materials ranging from metals and plastics to wood. The prototype’s purpose, anticipated attributes, and financial considerations guide the material selection, which is crucial for the end product’s performance and appearance.
Actual Machining
Armed with the G-code directions and the selected material, the CNC machine gets to work. It employs a suite of tools and maneuvers on different planes to sculpt the material. The culmination is a tangible prototype that is a near-perfect reflection of its digital counterpart.
Significance of CNC Machined Prototypes
CNC Machined Prototypes hold paramount significance in the modern manufacturing landscape, and here’s why:
Swift Idea-to-Prototype Transition
One of the hallmarks of CNC machining is its rapid prototyping capability. Once a design is digitized, it can be brought to life in a matter of hours or days, depending on complexity. This accelerated process aids in faster decision-making and shortens time-to-market.
Unparalleled Accuracy & Repeatability
CNC machines follow precise digital instructions, ensuring that every prototype produced mirrors its design with astounding accuracy. Furthermore, the process is highly repeatable; whether it’s the first unit or the thousandth, each prototype will maintain consistent quality and precision.
Material Versatility
With CNC machining, there’s no need to compromise on material choice. Be it metals, plastics, or woods, these machines can handle a wide variety, allowing designers to choose materials that best fit the prototype’s functional requirements and aesthetic appeal.
Achievement of Complex Geometries
Traditional manufacturing methods often fall short when intricate designs are on the table. CNC machines excel here, as they can produce prototypes with complex geometries, undercuts, and fine details that would otherwise be challenging or impossible.

Advantages of CNC Prototyping Over Traditional Methods
CNC Machined Prototypes have ushered in a new era of manufacturing, boasting advantages that set it apart from traditional methods:
Precision and consistency
Compared to manual machining, CNC prototyping offers superior precision. Every movement is computer-controlled, eliminating human error and ensuring consistency across multiple iterations of a prototype.
Cost-Effectiveness
While CNC machines involve a significant upfront investment, they can be more cost-effective in the long run. Traditional methods might require specialized tools or molds for each prototype, but CNC machines utilize digital designs, potentially reducing tooling costs. In scenarios with large production runs or intricate designs, savings become evident.
Speedy Turnaround
CNC prototyping can deliver results faster than many conventional techniques. Once a design is digitized, production can commence immediately, facilitating rapid iterations and faster product development cycles.
Scalability
One of CNC prototyping’s standout benefits is its scalability. The transition from a single prototype to mass production is smooth. Unlike methods that might require new molds or setups for large-scale production, CNC machines can replicate the prototype process effortlessly, ensuring each product remains true to the original design.
Real-world Applications
CNC machined prototypes have paved the way for groundbreaking innovations across diverse sectors:
Aerospace
The demand for lightweight, durable components is paramount. A notable instance is the development of turbine blades. Initially prototyped using CNC machining, these blades underwent rigorous testing and refinements before mass production, ensuring aircraft efficiency and safety.
Automotive
Car manufacturers employ CNC prototypes extensively, from engine components to intricate dashboard designs. The Tesla Roadster, for instance, utilized CNC prototyping for many of its parts, ensuring precision and optimal performance.
Medical
The medical sector’s need for bespoke tools and components is evident. CNC prototypes have been crucial in the development of surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and even dental crowns, enabling customization and rapid adaptations based on patient or practitioner needs.
Looking to the Future
Peering into the future of CNC machining reveals a horizon bustling with innovation and synergy:
Technological Integration
The fusion of CNC machining with technologies like 3D printing is set to redefine manufacturing. Imagine a world where a single machine offers both additive (3D printing) and subtractive (CNC machining) capabilities, allowing for intricate designs and superior finishes.
Software & Hardware Evolution
Advancements in CNC software promise more user-friendly interfaces, real-time monitoring, and enhanced machine learning capabilities. On the hardware front, we can anticipate machines with greater speed, precision, and multi-material compatibility, catering to an even wider array of projects.
Sustainability in Focus
The future beckons a greener approach to CNC prototyping. Efforts will intensify to reduce material wastage, adopt recycled materials, and optimize energy consumption. As sustainability becomes a global priority, CNC machining will pivot towards practices that are both eco-friendly and economically viable.
CONCLUSION
CNC Machined Prototypes have undeniably revolutionized the realm of manufacturing and prototyping, merging digital prowess with tangible outputs. Its adaptability, precision, and rapid response time have made it a keystone in sectors ranging from aerospace to medical. As we stand on the cusp of further technological integration, with 3D printing and advances in both software and hardware, the future of CNC promises even greater efficiency and innovation. Moreover, as the world leans towards sustainable practices, CNC machining is set to play a pivotal role in crafting a greener manufacturing landscape. In essence, CNC machined prototypes are not just a reflection of modern-day ingenuity but a beacon for the future of advanced manufacturing.





